|
 Downloads
Downloads
|
 Prices
Prices
|
 Videos
Videos
|
GeolOil - The Modified Simandoux Equation for Water Saturation
The Modified Simandoux Equation is an extension of the equation for shaly rocks to cover the cases where the saturation exponent n ≠ 2. The Simandoux equation of 1963 was one of the first models to successfully incorporate and correct the excess of conductivity in the matrix due to the presence of dispersed clays (the Archie equation of 1942 over-estimates amount of water saturation if there are clays). In its common standard version by Bardon and Pied (1969), the equation is:
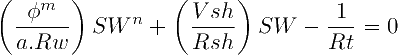
notice that if n=2, the equation takes the form of a second degree polynomial a.x2 + b.x + c = 0 on x=SW, which solution is the regular Simandoux equation. Also, the porosity to be used in the model, is the effective porosity φe corrected for shale content, not the total porosity φT.
When n≠2, the modified Simandoux equation can be solved by recursive numerical iterations. Start with an approximate guessed solution for SW, like the value found from the regular Simandoux equation, and keep iterating until convergence is reached within a desired numerical difference precision between SW and SWguess (usually 3-5 iterations are enough):
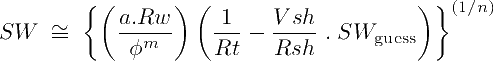
 PROOF OF THE SIMANDOUX EQUATION:
PROOF OF THE SIMANDOUX EQUATION:
Both the modified Simandoux equation (n≠2), and its regular version (n=2) can be deduced from the Archie equation rewritten in terms of true far field deep conductivity (1/Rt, the inverse of resistivity):
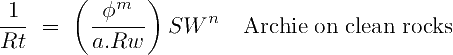
If the rock is shaly (Vsh ≥0), the deep conductivity (1/Rt) must be higher than the Archie conductivity because the clays transmit some electricity:
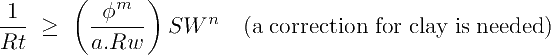
The excess on conductivity can be adjusted with a positive correction term χ:
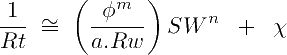
Now this eχtra χ term correction can be modeled as a function χ = χ (Rsh, Vsh, SW). Bardon and Pied (1969) considered that χ should increase proportionately with shale conductivity (1/Rsh) and the volume of shale (VSH). So they proposed: χ ≈ Vsh . SW . (1/Rsh). This conduces to the modified Simandoux equation in terms of conductivity:
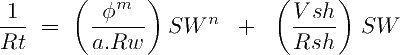
The Simandoux equation is usually the default option to work with shaly rocks. However, many clastic reservoirs with "fresh" salinities of less than 20,000 PPM equiv. NaCl behave better with the Indonesia equation.
As a general rule, we recommend to consider the use of the Indonesia equation for reservoirs with fresh formation waters, the Simandoux equation for salty reservoirs, and to explore the Fertl equation around α=0.30 if Rsh can not be determined because a pure nearby shale body can not be found in the reservoir.
Closed Equation variations for the modified Simandoux model
There are many ways to modify the regular Simandoux equation to become with closed, non-iterative approximations that work well for most of the cases. We show here two fundamental variations: The first variation takes the regular Simandoux equation and avoids iterations by using a custom exponent (2/n), in same style as the Indonesia equation:
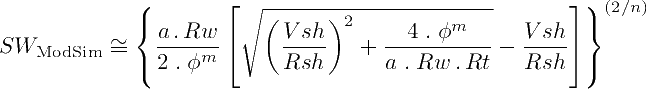
The second variation not only uses the Bardon and Pied (1969) χ conductivity term and the custom exponent (2/n). It also applies an inflation factor 1/(1-Vsh) to the Archie conductivity term:
 GeolOil is listed by the official
SPWLA software directory
GeolOil is listed by the official
SPWLA software directory
| |



|
|
|
© 2012-2026 GeolOil LLC. Please link or refer us under Creative Commons License CC-by-ND |



 TRAINING
TRAINING

 PAPERS
PAPERS
 REFERENCES
REFERENCES
 GET IN TOUCH
GET IN TOUCH